
In diesem Tutorial zeigen wir Ihnen, wie Sie einen Reverse-Proxy einrichten. Für diejenigen unter Ihnen, die es nicht wussten:Ein Nginx-HTTPS-Reverse-Proxy ist ein zwischengeschalteter Proxy-Dienst, der einen Client übernimmt Anfrage, leitet sie an einen oder mehrere Server weiter und liefert anschließend die Antwort des Servers zurück an den Client. Wenn Sie mehrere Server haben, kann ein Reverse-Proxy dabei helfen, die Last zwischen den Servern auszugleichen und die Leistung zu verbessern Kontakt für Kunden, kann es die Protokollierung und Berichterstellung über mehrere Server hinweg zentralisieren.
Dieser Artikel geht davon aus, dass Sie zumindest über Grundkenntnisse in Linux verfügen, wissen, wie man die Shell verwendet, und vor allem, dass Sie Ihre Website auf Ihrem eigenen VPS hosten. Die Installation ist recht einfach und setzt Sie voraus im Root-Konto ausgeführt werden, wenn nicht, müssen Sie möglicherweise 'sudo hinzufügen ‘ zu den Befehlen, um Root-Rechte zu erhalten. Ich zeige Ihnen Schritt für Schritt, wie Sie einen Reverse-Proxy einrichten.
Voraussetzungen
- Ein Server, auf dem eines der folgenden Betriebssysteme ausgeführt wird:CentOS oder Ubuntu Linux.
- Es wird empfohlen, dass Sie eine neue Betriebssysteminstallation verwenden, um potenziellen Problemen vorzubeugen.
- Ein
non-root sudo useroder Zugriff auf denroot user. Wir empfehlen, alsnon-root sudo userzu agieren , da Sie Ihr System beschädigen können, wenn Sie als Root nicht aufpassen.
Nginx-Reverse-Proxy einrichten
Schritt 1. Beginnen wir zunächst damit, sicherzustellen, dass Ihr System auf dem neuesten Stand ist.
sudo dnf update
Schritt 2. Nginx auf dem Linux-System installieren.
- Die Installation von Nginx unter CentOS 8 ist so einfach wie das Eingeben von:
sudo dnf install nginx
- Die Installation von Nginx auf Ubuntu 20.04 LTS ist so einfach wie das Eingeben von:
sudo apt install nginx
Sobald die Installation abgeschlossen ist, aktivieren und starten Sie den Nginx-Dienst:
sudo systemctl enable nginx sudo systemctl start nginx
Navigieren Sie zu http://localhost in Ihrem Browser, um zu überprüfen, ob der Webserver wie erwartet läuft:
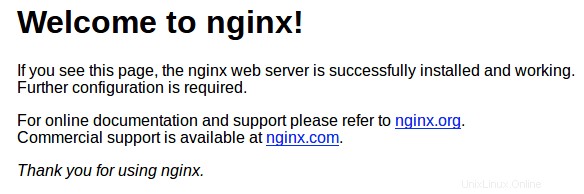
Schritt 3. Nginx Reverse Proxy einrichten.
Befolgen Sie zuerst den folgenden Befehl, um den virtuellen Host zu deaktivieren:
sudo unlink /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
Wir müssen eine Datei innerhalb von /etc/nginx/sites-available erstellen Verzeichnis, das die Reverse-Proxy-Informationen enthält. Wir können diese reverse-proxy.conf nennen zum Beispiel:
nano reverse-proxy.conf
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.77.20;
}
} Der wichtige Teil hier ist der proxy_pass Direktive, die im Wesentlichen angibt, dass alle Anfragen, die durch den Nginx-Reverse-Proxy kommen, an den Apache-Remote-Socket 192.168.77.20:80 weitergeleitet werden sollen.
Sobald Sie die entsprechenden Anweisungen zu Ihrer .conf hinzugefügt haben Datei, aktivieren Sie sie, indem Sie auf /sites-enabled/ verlinken mit dem folgenden Befehl:
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/reverse-proxy.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/reverse-proxy.conf
Testen Sie die Nginx-Konfigurationsdatei:
$ sudo nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Zuletzt müssen wir einen Nginx-Konfigurationstest durchführen und Nginx neu starten, um seine Leistung zu überprüfen:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Schritt 4. Nginx Reverse Proxy mit Let’s Encrypt.
Führen Sie diese Befehle in der Befehlszeile auf dem Computer aus, um Certbot zu installieren:
wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto sudo mv certbot-auto /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto sudo chown root /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto sudo chmod 0755 /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
Führen Sie dann diesen Befehl aus, um ein Zertifikat zu erhalten und Certbot Ihre Nginx-Konfiguration automatisch bearbeiten zu lassen:
sudo /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto --nginx
Das Ergebnis sieht wie folgt aus:
Creating virtual environment... Installing Python packages... Installation succeeded. Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): your@email.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (A)gree/(C)ancel: A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y Which names would you like to activate HTTPS for? - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: your-domain.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate numbers separated by commas and/or spaces, or leave input blank to select all options shown (Enter 'c' to cancel): 1 Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for your-domain-a.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/reverse-proxy.conf Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2 Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/reverse-proxy.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://your-domain.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=your-domain.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2020-08-03. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot-auto again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot-auto renew" - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so making regular backups of this folder is ideal. - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Herzlichen Glückwunsch! Sie haben erfolgreich einen Reverse-Proxy eingerichtet. Vielen Dank, dass Sie dieses Tutorial zum Einrichten eines Nginx-Reverse-Proxy auf dem Linux-System verwendet haben. Für zusätzliche Hilfe oder nützliche Informationen empfehlen wir Ihnen, die offizielle Nginx-Website.