Sandstorm ist eine kostenlose Open-Source-Plattform für Webanwendungen und Server. Mit Sandstorm können Sie viele Anwendungen bereitstellen, darunter WordPress, GitLab, MediaWiki, Apache Wave und RoundCube-Webmail. Es verfügt über eine einfache und benutzerfreundliche Weboberfläche, mit der Sie Apps auf Ihrem Server installieren und verwalten können. Im Vergleich zu anderen Plattformen ist Sandstorm von Grund auf so konzipiert, dass es radikal einfacher zu bedienen ist.
In diesem Beitrag zeigen wir Ihnen, wie Sie Sandstorm auf CentOS 8 VPS installieren.
Voraussetzungen
- Ein frischer CentOS 8-Server auf der Atlantic.Net Cloud Platform
- Ein auf Ihrem Server konfiguriertes Root-Passwort
Schritt 1 – Atlantic.Net Cloud-Server erstellen
Melden Sie sich zunächst bei Ihrem Atlantic.Net Cloud Server an. Erstellen Sie einen neuen Server und wählen Sie CentOS 8 als Betriebssystem mit mindestens 2 GB RAM. Stellen Sie über SSH eine Verbindung zu Ihrem Cloud-Server her und melden Sie sich mit den oben auf der Seite hervorgehobenen Anmeldeinformationen an.
Sobald Sie sich bei Ihrem CentOS 8-Server angemeldet haben, führen Sie den folgenden Befehl aus, um Ihr Basissystem mit den neuesten verfügbaren Paketen zu aktualisieren.
dnf update -y
Schritt 2 – Hostnamen einrichten
Bevor Sie beginnen, müssen Sie einen vollständig qualifizierten Hostnamen Ihres Servers festlegen. Sie können es mit dem folgenden Befehl festlegen:
hostnamectl set-hostname sandstorm.example.com
Sobald Sie fertig sind, können Sie mit dem nächsten Schritt fortfahren.
Schritt 3 – Sandstorm installieren
Sandstorm stellt ein Skript für die automatische Installation bereit, das die Installation von Sandstorm auf Ihrem Server vereinfacht.
Sie können das Sandstorm-Installationsskript mit dem folgenden Befehl herunterladen:
curl https://install.sandstorm.io >install.sh
Führen Sie nach dem Herunterladen des Skripts das heruntergeladene Skript aus, um die Installation zu starten:
bash install.sh
Sie werden aufgefordert, die Installationsoption wie unten gezeigt auszuwählen:
Sandstorm makes it easy to run web apps on your own server. You can have: 1. A typical install, to use Sandstorm (press enter to accept this default) 2. A development server, for working on Sandstorm itself or localhost-based app development
Drücken Sie Eingabe um die Standardoption auszuwählen. Sie sollten die folgende Ausgabe sehen:
How are you going to use this Sandstorm install? [1] We're going to: * Install Sandstorm in /opt/sandstorm * Automatically keep Sandstorm up-to-date * Create a service user (sandstorm) that owns Sandstorm's files * Configure Sandstorm to start on system boot (with systemd) * Listen for inbound email on port 25. Rest assured that Sandstorm itself won't run as root. OK to continue? [yes]
Drücken Sie Eingabe weitermachen. Sie sollten die folgende Ausgabe sehen:
NOTE: It looks like your system already has some other web server installed
(port 80 and/or 443 are taken), so Sandstorm cannot act as your main
web server.
This script can set up Sandstorm to run on port 6080 instead,
without HTTPS. This makes sense if you're OK with typing the port number
into your browser whenever you access Sandstorm and you don't need
security. This also makes sense if you are going to set up a reverse proxy;
if so, see https://docs.sandstorm.io/en/latest/administering/reverse-proxy/
If you want, you can quit this script with Ctrl-C now, and go uninstall
your other web server, and then run this script again. It is also OK to
proceed if you want.
OK to skip automatic HTTPS setup & bind to port 6080 instead? [yes]
Drücken Sie Eingabe um den Sandstorm-Port an 6080 zu binden . Sie sollten die folgende Ausgabe sehen:
Note: Sandstorm's storage will only be accessible to the group 'sandstorm'. As a Sandstorm user, you are invited to use a free Internet hostname as a subdomain of sandcats.io, a service operated by the Sandstorm development team. ... Sandcats.io protects your privacy and is subject to terms of use. By using it, you agree to the terms of service & privacy policy available here: https://sandcats.io/terms https://sandcats.io/privacy Choose your desired Sandcats subdomain (alphanumeric, max 20 characters). Type the word none to skip this step, or help for help. What *.sandcats.io subdomain would you like? [] none
Geben Sie none ein und drücken Sie Enter . Sobald die Installation abgeschlossen ist, sollten Sie die folgende Ausgabe sehen:
URL users will enter in browser: [http://sandstorm.example.com:6080] Sandstorm requires you to set up a wildcard DNS entry pointing at the server. This allows Sandstorm to allocate new hosts on-the-fly for sandboxing purposes. Please enter a DNS hostname containing a '*' which maps to your server. For example, if you have mapped *.foo.example.com to your server, you could enter "*.foo.example.com". You can also specify that hosts should have a special prefix, like "ss-*.foo.example.com". Note that if your server's main page is served over SSL, the wildcard address must support SSL as well, which implies that you must have a wildcard certificate. For local-machine servers, we have mapped *.local.sandstorm.io to 127.0.0.1 for your convenience, so you can use "*.local.sandstorm.io" here. If you are serving off a non-standard port, you must include it here as well. Wildcard host: [*.sandstorm.example.com:6080] Your server is now online! Visit this link to start using it: http://sandstorm.example.com:6080/setup/token/7f7f36c9e39f738a69564622123be64b373141a5 NOTE: This URL expires in 15 minutes. You can generate a new setup URL by running 'sudo sandstorm admin-token' from the command line. To learn how to control the server, run: sandstorm help
An diesem Punkt ist Sandstorm installiert und überwacht Port 6080. Sie können dies mit dem folgenden Befehl überprüfen:
ss -antpl | grep 6080
Sie sollten die folgende Seite sehen:
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:6080 0.0.0.0:* users:(("sandstorm/gtway",pid=28336,fd=7),("sandstorm/montr",pid=28265,fd=7),("sandstorm/top",pid=28262,fd=7))
Schritt 4 – Greifen Sie auf die Sandstorm-Web-Benutzeroberfläche zu
Öffnen Sie nun Ihren Webbrowser und greifen Sie über die URL http://sandstorm.example.com:6080/setup/token/7f7f36c9e39f738a69564622123be64b373141a5 auf Sandstorm zu . Sie werden auf die folgende Seite weitergeleitet:
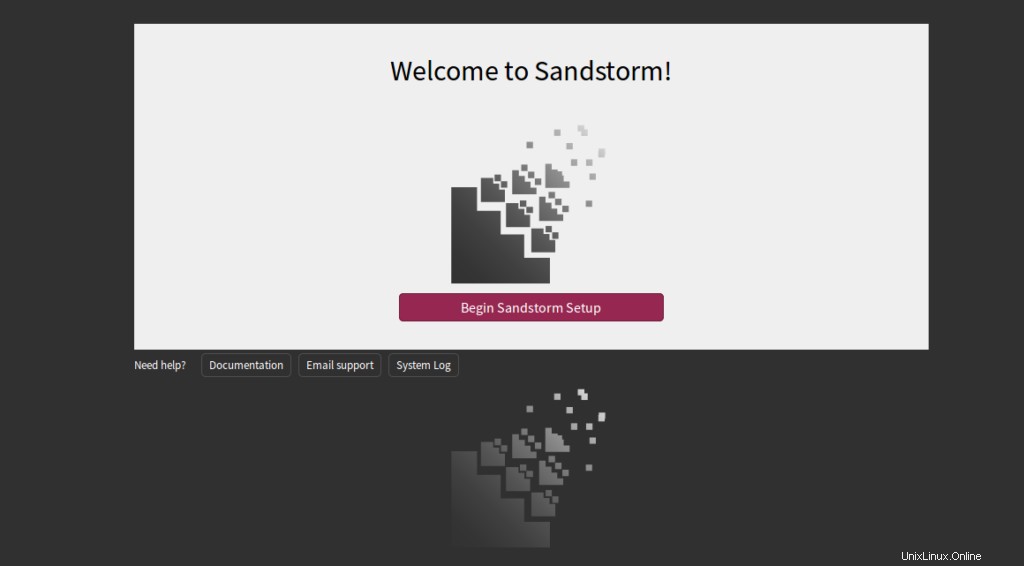
Klicken Sie auf Begin Sandstorm Setup . Sie sollten die folgende Seite sehen:
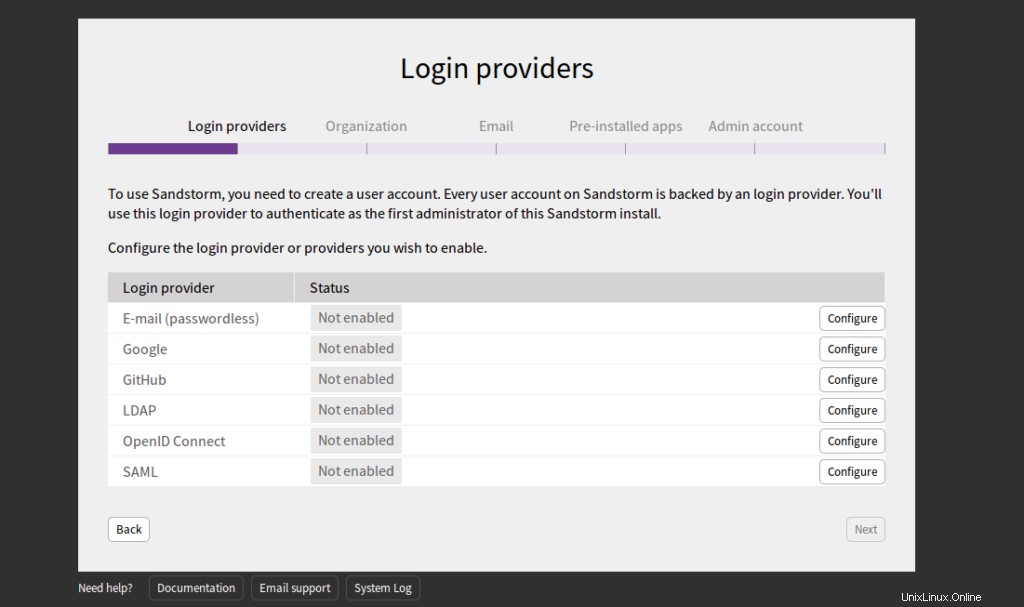
Wählen Sie E-Mail und klicken Sie auf Konfigurieren Taste. Sie sollten die folgende Seite sehen:
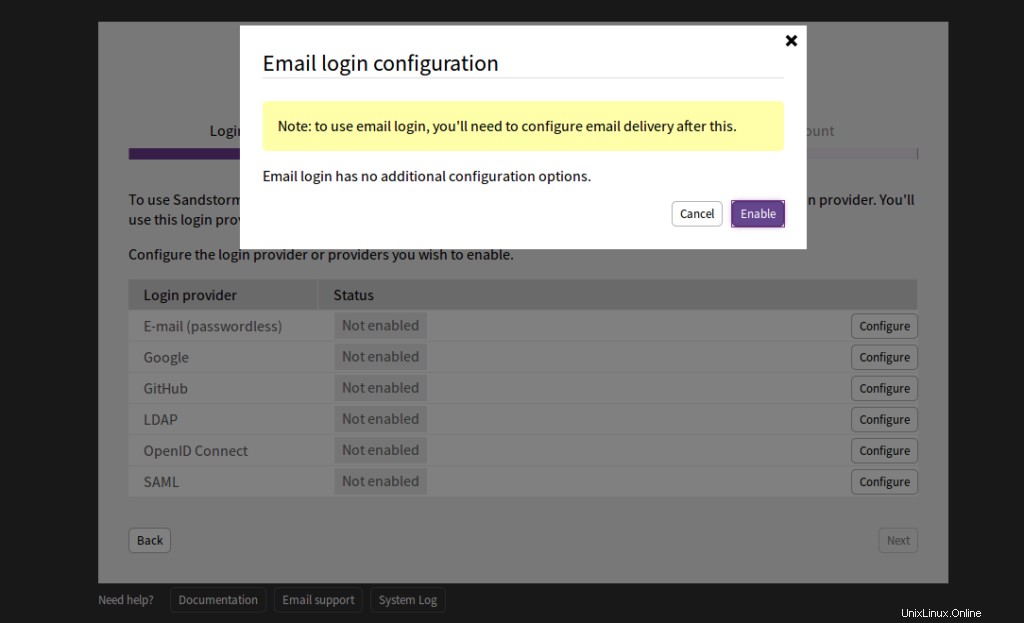
Klicken Sie auf Aktivieren . Sie sollten die folgende Seite sehen:
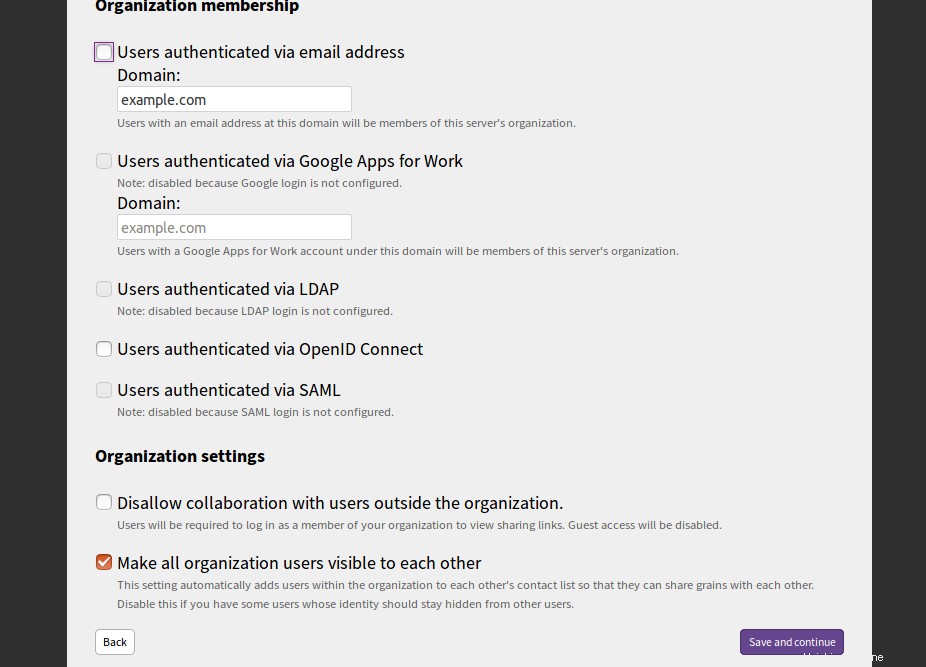
Geben Sie Ihre Mailserver-Domain an und klicken Sie auf Speichern und fortfahren Taste. Sie sollten die folgende Seite sehen:
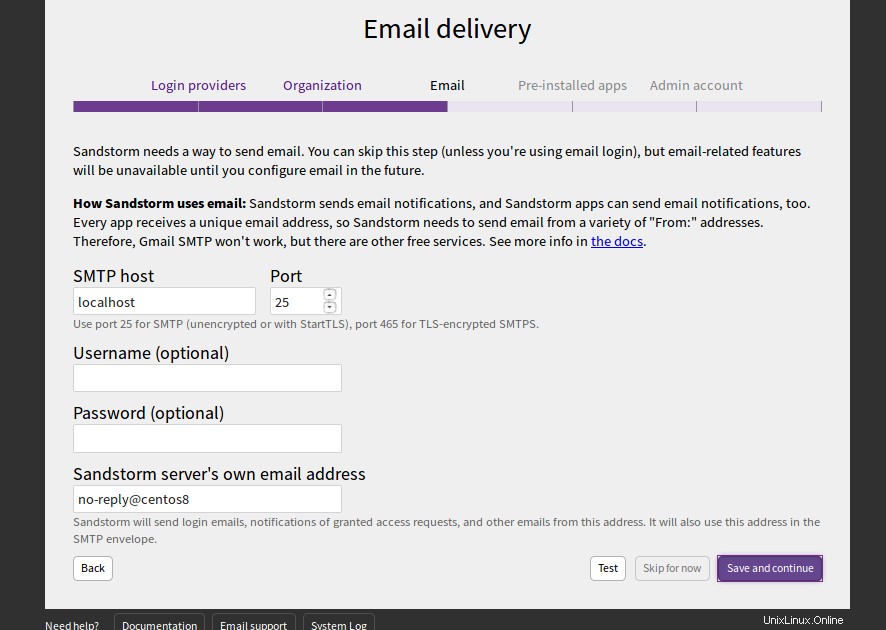
Geben Sie Ihren SMTP-Host, Port, Benutzernamen und Passwort an und klicken Sie auf Speichern und weiter Taste. Sie sollten die folgende Seite sehen:
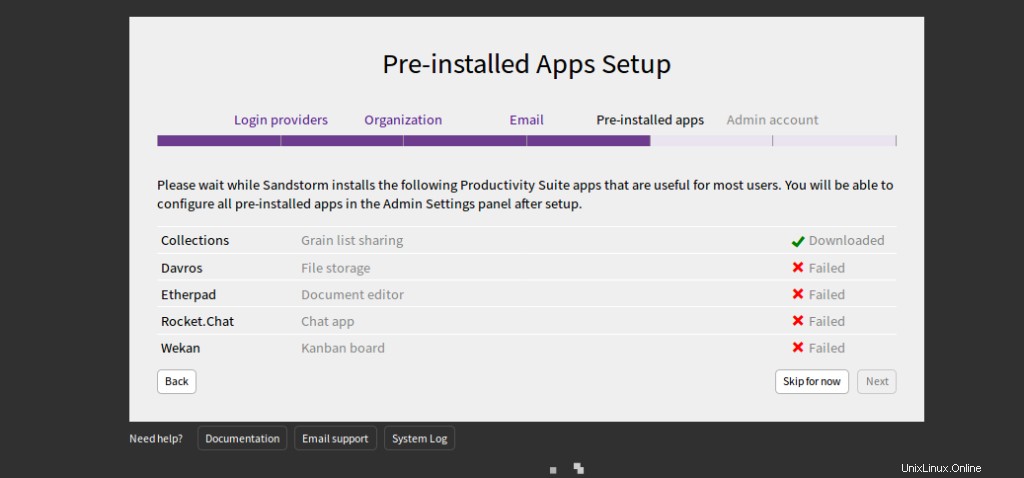
Klicken Sie auf Vorerst überspringen . Sie sollten die folgende Seite sehen:
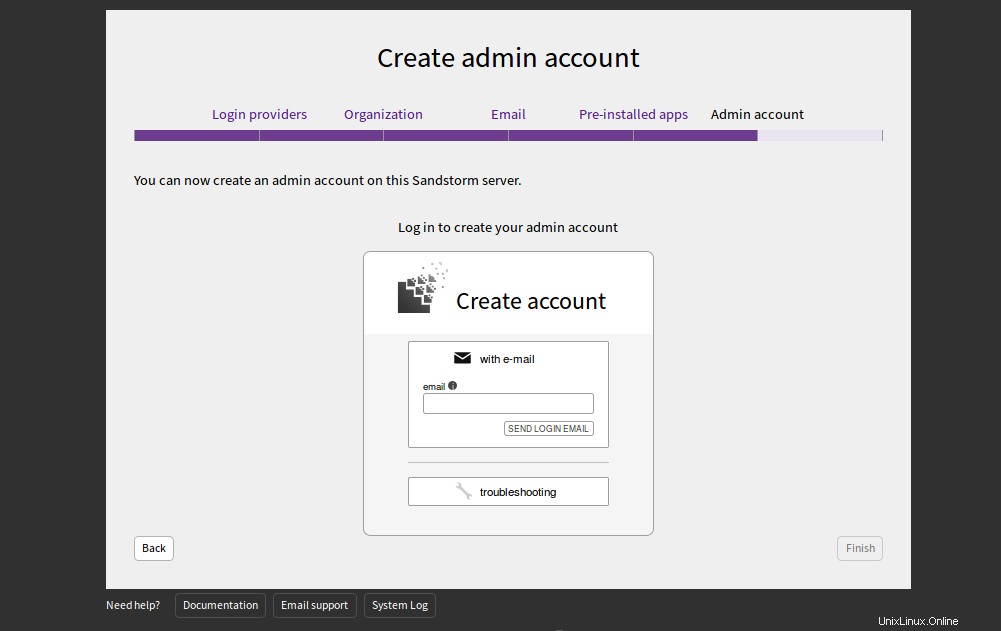
Geben Sie Ihre E-Mail-Adresse an und klicken Sie auf LOGIN-EMAIL SENDEN. Sie sollten eine E-Mail mit Anmeldeinformationen erhalten. Sie können diese Anmeldeinformationen verwenden, um sich beim Sandstorm-Server anzumelden.
Schlussfolgerung
Herzliche Glückwünsche! Sie haben Sandstorm erfolgreich auf CentOS 8 VPS installiert. Sandstorm ist ein sehr nützliches Tool für Entwickler. Es hilft ihnen, jede App mit nur einem Klick bereitzustellen. Weitere Informationen und Dokumentation zu Sandstorm finden Sie in der Dokumentation.