MariaDB ist eines der beliebtesten Open-Source-Datenbankverwaltungssysteme, das von kleinen bis großen Unternehmen verwendet wird. Es ist eine Abzweigung des berühmten Datenbankservers MySQL, entwickelt von MariaDB Corporation Ab, geführt von den ursprünglichen Entwicklern von MySQL.
MariaDB ist vollständig kompatibel mit MySQL, um eine Drop-In-Ersatzfunktion zu gewährleisten. MariaDB wird häufig als Datenbankserver im LAMP- und LEMP-Stack verwendet.
LESEN: So installieren Sie den LAMP-Stack unter CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
LESEN: So installieren Sie den LEMP-Stack auf CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
In diesem Beitrag werden wir sehen, wie MariaDB auf CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 installiert wird.
Installieren Sie MariaDB auf CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
Sie können MariaDB-Pakete für CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 auf zwei Arten erhalten.
- Red Hat-Repository (v10.3)
- Offizieller MariaDB-Mirror (v10.4)
Installieren Sie MariaDB aus dem AppStream-Repository
Die Installation von MariaDB aus dem AppStream-Repository ist unkompliziert. Aber das Repository hat möglicherweise eine etwas alte Version des MariaDB-Pakets.
yum -y install @mariadb
Installieren Sie MariaDB vom offiziellen MariaDB-Mirror
MariaDB Foundation bietet MariaDB-Pakete für CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 an. Von MariaDB bereitgestellte Pakete sind immer aktuell und werden von der MariaDB-Community unterstützt.
CentOS 8
cat <<EOF >> /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/centos8-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1 EOF
RHEL8
cat <<EOF >> /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/rhel8-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1 EOF
Installieren Sie den MariaDB-Server mit dem folgenden Befehl.
Wir müssen das rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms- und das AppStream-Repository vorübergehend auf RHEL 8 bzw. CentOS 8 deaktivieren, damit yum Pakete vom MariaDB-Mirror herunterladen kann.### CentOS 8 ### yum install -y boost-program-options yum --disablerepo=AppStream install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-client ### RHEL 8 ### yum --disablerepo=rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-client
MariaDB-Dienst verwalten
Falls Sie den MariaDB-Dienst starten/stoppen möchten, können Sie die folgenden Befehle verwenden.
systemctl start mariadb systemctl stop mariadb
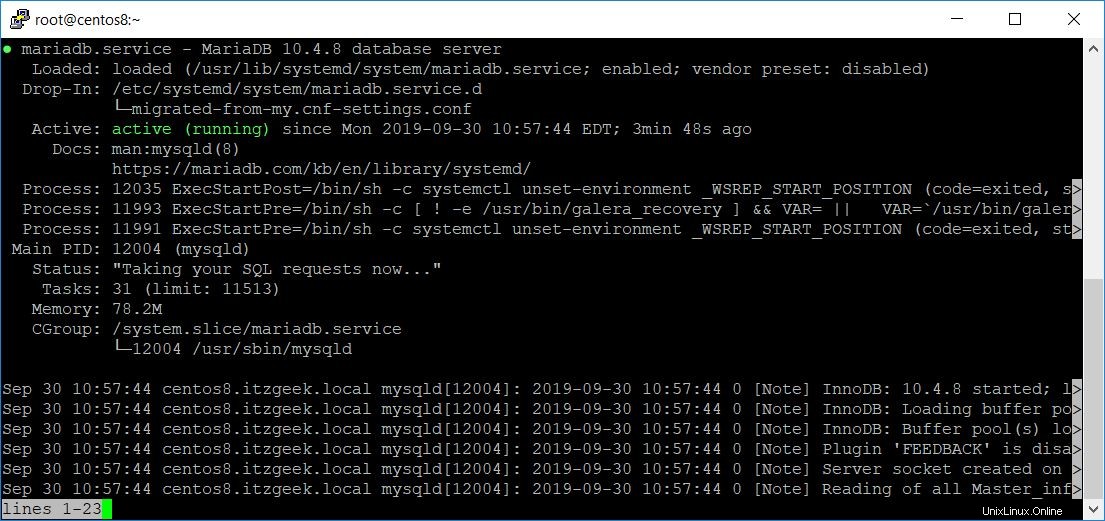
Überprüfen Sie, ob MariaDB ausgeführt wird oder nicht.
systemctl status mariadb
Sichere MariaDB-Installation
Verwenden Sie den Befehl mysql_secure_installation, um die Ersteinrichtung des MariaDB-Servers durchzuführen. Es wird empfohlen, diesen Befehl auf Produktionsservern auszuführen. Es entfernt anonyme Benutzer, Testdatenbanken und verbietet Remote-Root-Login.
mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
haven't set the root password yet, you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): << Just Press Enter
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password or using the unix_socket ensures that nobody
can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] N << Disable Unix Socket Authendication to Enable Password Authentication
... skipping.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Change the root password? [Y/n] Y << Set MariaDB root password
New password: << Enter root password
Re-enter new password: << Re-Enter root password
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y << Remove Anonymous user
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y << Disallow root login remotely
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y << Remove test database
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y << Reload privilege tables
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Zugriff auf MariaDB
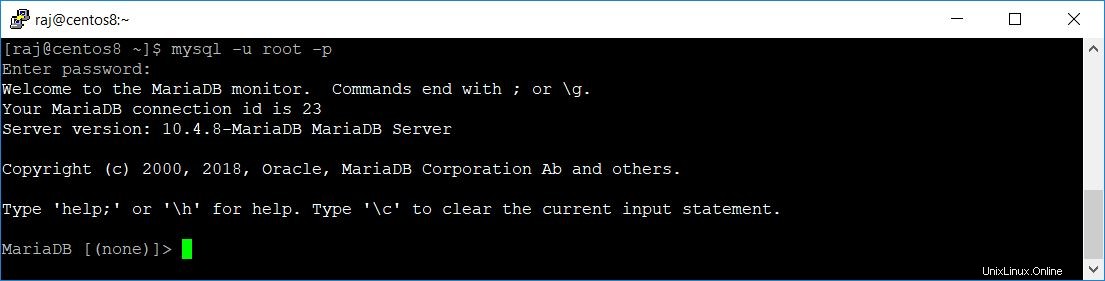
Melden Sie sich mit dem folgenden Befehl beim MariaDB-Server an.
mysql -u root -pPasswort erforderlich
Schlussfolgerung
Das ist alles. In diesem Beitrag haben Sie gelernt, wie Sie MariaDB auf CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 installieren und die Ersteinrichtung durchführen. Lesen Sie die MariaDB-Artikel für Anfänger, um mehr über die Arbeit mit MariaDB zu erfahren.