Let’s Encrypt ist eine weithin bekannte Zertifizierungsstelle, die kostenlose SSL-Zertifikate für Websites bereitstellt und im April 2016 eingeführt wurde.
Mit Hilfe des Certbot-Clients werden die Zertifikatserstellung, -validierung, -signierung, -implementierung und -erneuerung von Zertifikaten vollständig automatisiert.
Voraussetzungen
Folgen Sie den Links, um entweder den LAMP-Stack oder nur den Apache-Webserver auf Ihrem System zu installieren.
LESEN :So installieren Sie den LAMP-Stack unter CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
LESEN :So installieren Sie den LAMP-Stack unter CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
Certbot-Client installieren
Um ein Zertifikat für eine beliebige Domäne zu generieren und zu installieren, sollten Sie über Terminalzugriff verfügen und den Certbot ACME-Client auf dem System installiert haben. Der Certbot-Client automatisiert die Ausstellung und Installation von Zertifikaten ohne Ausfallzeiten.
Der Certbot-Client ist im EPEL-Repository für CentOS 7/RHEL 7 verfügbar. Wir müssen den Certbot-Client für CentOS 8/RHEL 8 jedoch manuell von seiner offiziellen Website herunterladen.
### CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 ### yum install -y httpd mod_ssl curl -O https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto mv certbot-auto /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto chmod 0755 /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto ### CentOS 7 ### rpm -ivh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm yum install -y certbot python2-certbot-apache ### RHEL 7 ### rpm -ivh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-optional-rpms yum install -y certbot python2-certbot-apache
Virtuellen Host erstellen
Wir erstellen einen virtuellen Host für die Domain:www.itzgeek.net.
Dieser virtuelle Host verwaltet die HTTP-Version Ihrer Domain.vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/www.itzgeek.net.conf
Verwenden Sie die folgenden Informationen.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName itzgeek.net
ServerAlias www.itzgeek.net
DocumentRoot /var/www/www.itzgeek.net
<Directory /var/www/www.itzgeek.net>
Options -Indexes +FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/www.itzgeek.net-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/www.itzgeek.net-access.log combined
</VirtualHost> Erstellen Sie einen Dokumentenstamm, um Ihre HTML-Dateien zu platzieren.
mkdir -p /var/www/www.itzgeek.net
Platzieren Sie die HTML-Datei im Dokumentenstammverzeichnis Ihrer Domain.
echo "This is a test site @ www.itzgeek.net" > /var/www/www.itzgeek.net/index.html
Ändern Sie die Berechtigung des Verzeichnisses.
chown -R apache:apache /var/www/www.itzgeek.net
Starten Sie den Apache-Dienst neu.
systemctl restart httpd
DNS-Eintrag erstellen/aktualisieren
Gehen Sie zu Ihrem Domain-Registrar und erstellen Sie einen A/CNAME-Eintrag für Ihre Domain. Beispiel:www.itzgeek.net.
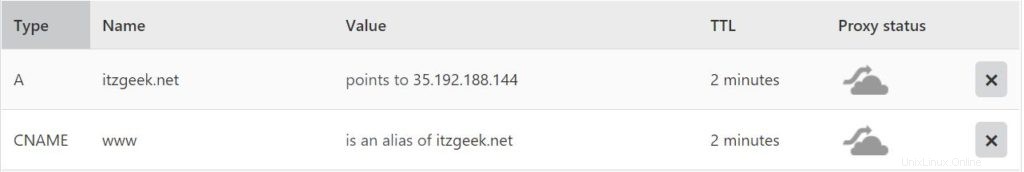
Warten Sie einige Zeit, bis der Datensatz weitergegeben wird.
Überprüfen Sie die DNS-Weitergabe mit dem Dienstprogramm Nslookup yum install -y bind-utils.

Installieren Sie das SSL-Zertifikat von Let’s Encrypt
Verwenden Sie den Befehl certbot, um das Let’s Encrypt-Zertifikat zu generieren und zu installieren.
### RHEL 8 ### /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto --apache ### CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 ### certbot --apache
Folgen Sie der interaktiven Aufforderung und installieren Sie das Zertifikat.
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): itzgeek.web@gmail.com << Enter Email address to receive notifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (A)gree/(C)ancel: A << Agree to Terms of Sevice - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y << Subscribe to Newsletter Which names would you like to activate HTTPS for? - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: itzgeek.net 2: www.itzgeek.net - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate numbers separated by commas and/or spaces, or leave input blank to select all options shown (Enter 'c' to cancel): 2 << Choose the domain to install Let's Encrypt SSL certificate Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for www.itzgeek.net Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Created an SSL vhost at /etc/httpd/conf.d/www.itzgeek.net-le-ssl.conf Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/httpd/conf.d/www.itzgeek.net-le-ssl.conf Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2 << Redirect from HTTP to HTTPS Redirecting vhost in /etc/httpd/conf.d/www.itzgeek.net.conf to ssl vhost in /etc/httpd/conf.d/www.itzgeek.net-le-ssl.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://www.itzgeek.net You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=www.itzgeek.net - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.itzgeek.net/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.itzgeek.net/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2019-11-10. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot-auto again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot-auto renew" - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so making regular backups of this folder is ideal. - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Firewall
Konfigurieren Sie die Firewall so, dass HTTPS-Anfragen zugelassen werden.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=443/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
Verifizieren Sie das Let’s Encrypt-Zertifikat
Überprüfen Sie das Let’s Encrypt-Zertifikat, indem Sie die HTTPS-Version Ihrer Website aufrufen.
http://Ihre-http-WebsiteODER
https://Ihre-https-WebsiteSie sollten jetzt eine HTTPS-Version Ihrer Website erhalten.
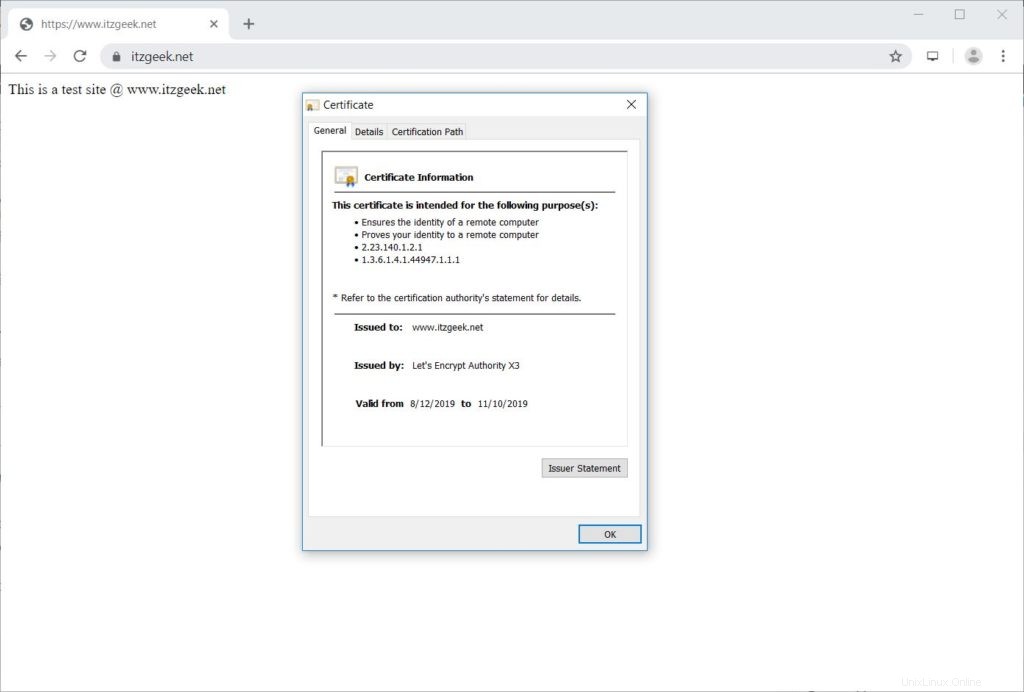
Let’s Encrypt SSL-Zertifikat testen
Testen Sie Ihr SSL-Zertifikat auf Probleme und seine Sicherheitsbewertungen, indem Sie zur folgenden URL gehen.
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=www.itzgeek.net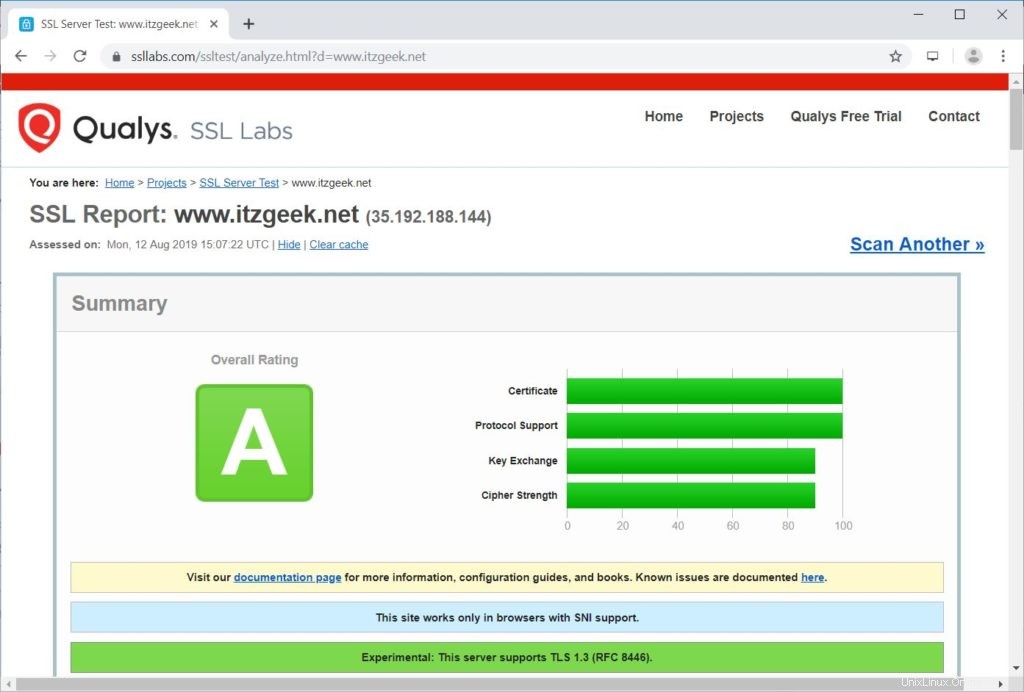
Erneuern Sie das Let’s Encrypt-Zertifikat
Das Let’s Encrypt-Zertifikat ist ab Ausstellungsdatum 90 Tage lang gültig und muss vor Ablauf verlängert werden.
In CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 erstellt der certbot-Client standardmäßig einen Cron-Scheduler-Eintrag, um Let’s Encrypt-Zertifikate automatisch zu erneuern.
Leider müssen wir für CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 den Cron-Scheduler manuell konfigurieren.
echo "0 0,12 * * * root python -c 'import random; import time; time.sleep(random.random() * 3600)' && /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto renew" | sudo tee -a /etc/crontab > /dev/null
Sie können den Zertifikaterneuerungsprozess auch mit dem folgenden Befehl simulieren, um sicherzustellen, dass die Erneuerung reibungslos verläuft.
### CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 ### /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto renew --dry-run ### CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 ### certbot renew --dry-runUm das Let’s Encrypt-Zertifikat zu erneuern, führen Sie den obigen Befehl ohne
--dry-run aus Möglichkeit. Ausgabe:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/www.itzgeek.net.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Cert not due for renewal, but simulating renewal for dry run Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache Renewing an existing certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for www.itzgeek.net Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - new certificate deployed with reload of apache server; fullchain is /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.itzgeek.net/fullchain.pem - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ** DRY RUN: simulating 'certbot renew' close to cert expiry ** (The test certificates below have not been saved.) Congratulations, all renewals succeeded. The following certs have been renewed: /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.itzgeek.net/fullchain.pem (success) ** DRY RUN: simulating 'certbot renew' close to cert expiry ** (The test certificates above have not been saved.) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
Wenn die Ausgabe kein Problem meldet, funktioniert die Zertifikatserneuerung wie erwartet.
Schlussfolgerung
Das ist alles. Ich hoffe, Sie haben gelernt, wie Sie das SSL-Zertifikat Let’s Encrypt mit Apache unter CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 und CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 einrichten. Teilen Sie Ihr Feedback im Kommentarbereich mit.